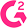Guide to Training Custom Interactive Instance Segmentation Model for Agricultural Images

We trained Instance Segmentation model for agricultural plant images and achieved remarkable results.

Table of Contents
Task Overview: Training a Model Using Selective Plant Instances
Sometimes it's tricky to do manual image segmentation. While AI can assist in streamlining the process, standard models may not always meet the demands of industrial settings, necessitating the training of a custom model.
This post will guide you through training an Interactive Instance Segmentation model in Supervisely using agricultural images of plants as an example. We will conduct a comparative analysis against publicly available pretrained models, showcasing the superior performance of our custom model.
Importantly, in our experiment, we departed from relying on a fully labeled dataset. Instead, we strategically chose to selectively label instances of plants based on our preferences, and remarkably, this approach proved successful.
We'll provide all the necessary tools, data, and guidelines for replicating the experiment's results or for you to follow the tutorial using your own dataset.
Video Tutorial
Watch a quick 5-minute video tutorial to learn the process of training models, utilizing instance segmentation, and gaining practical skills for more efficient labeling. The tutorial focuses on the agricultural sector, showcasing complex objects that demand precise marking.
We advise you to reproduce the process of creating a model yourself and see that this greatly speeds up the work of annotators.
Benefits of Custom Instance Segmentation Model
-
Efficiency in Annotation: Reduces the need to annotate every single object, significantly speeding up the annotation process.
-
Training Flexibility: Add new data into the training set and adjust object classes for more precise annotation.
-
Iterative Approach: Iterative learning enables enhancements in annotation quality and the addition of extra object classes, all without requiring the entire dataset to be reannotated.
Custom Instance Segmentation Models for Industry-Specific cases
Precise Instance Segmentation Models can be beneficial in various fields. However, publicly available pre-trained models are typically trained on common datasets like COCO, Pascal VOC, Cityscapes , making them less efficient for industry-specific data. This emphasizes the need for customizable models tailored to specific industrial use cases.
 Using a custom model to segment objects such as cracks in concrete, carrot sprouts, infrastructure, and wires on poles.
Using a custom model to segment objects such as cracks in concrete, carrot sprouts, infrastructure, and wires on poles.
Let's explore a few real-world examples:
- Medical Diagnosis: In medicine, custom instance segmentation models may be used to speed up the labeling on medical imagery, reducing analysis time and improving diagnostic accuracy. This acceleration not only reduces analysis time but also enhances diagnostic accuracy, empowering healthcare professionals with efficient tools.
- Infrastructure Inspection and Construction: In construction and infrastructure, custom instance segmentation tools contribute to precise image labeling, fostering improved project management and infrastructure assessment.
- Plant Phenotyping and Agriculture: In agriculture, accurate plant segmentation may be used for disease and defect detection, as well as yield estimation. By employing interactive image segmentation tools, agricultural practices can achieve greater precision in monitoring and optimizing plant health.
Training Custom Segmentation Model in Supervisely
Supervisely equips you with a powerful toolkit to streamline the entire training process. Explore the step-by-step process of training a customized model tailored to instance segmentation of specific agricultural plant images. Even if you lack programming skills, you can effortlessly customize models directly within the platform.
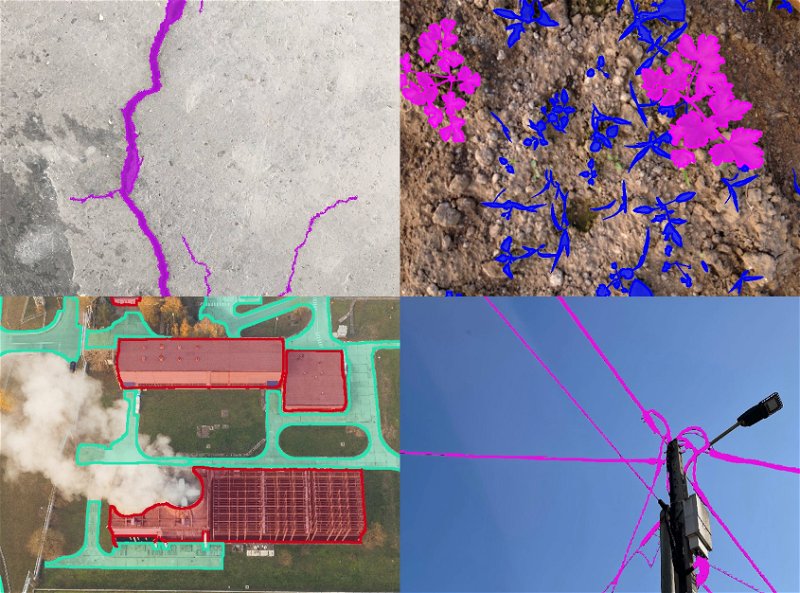
 The process of creating a custom Instance Segmentation Model.
The process of creating a custom Instance Segmentation Model.
Here is an overview of steps:
-
Сollect unlabeled images for training.
-
Strategically selectively label images that precisely represent the unique aspects of your task.
-
Run the Train RITM application on the project with labeled. Make sure to use specific settings in the application: select Instance segmentation and
crop then fit an instance objectoption. option. This ensures that only labeled objects are used for training. By doing so, you'll make the model more customizable to your use case. -
Deploy your model using the Serving App.
-
Leverage the newly created custom model to enhance both the speed and accuracy of the labeling process.
🔁 You can replicate step 2 with a new model to expand the dataset size and enhance model performance.
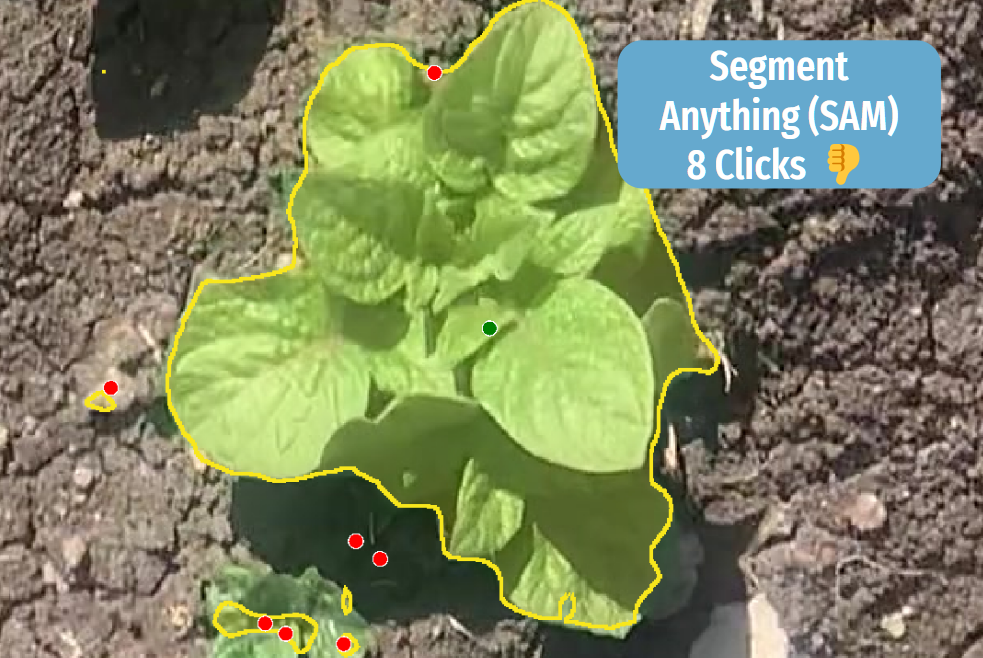
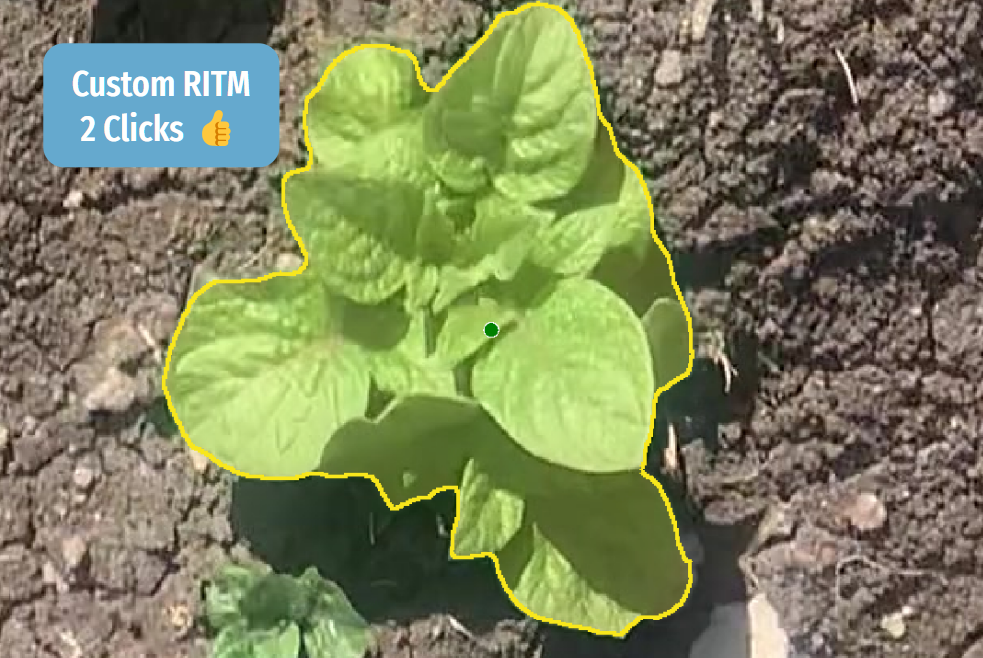
Benchmark: Pretrained vs. Custom Models
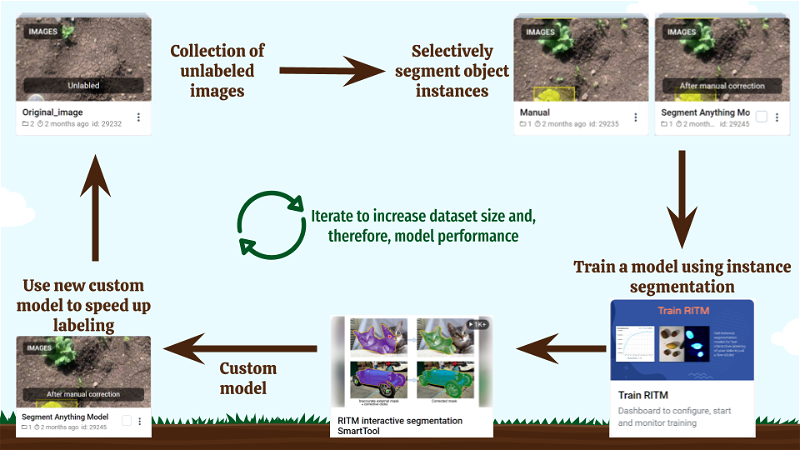
We compared the performance of the pretrained SAM, RITM and custom RITM models using a data set consisting of 50 objects, including 25 potato plants and 25 weed plants.
| Method | Manual | RITM | SAM | Custom RITM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Clicks | 7122 | 278 | 237 | 18 |
| Time in SmartTool | - | 19 mins | 23 mins | 12 mins |
| Correction Clicks | - | 615 | 2840 | 163 |
| Correction time | - | 10 mins | 40 mins | 3 mins |
| Total Time on the Dataset | 190 mins | 32 mins | 66 mins | 18 mins |
From the presented data, it is evident that the custom RITM model has outperformed the manual annotation, as well as SAM, and the standard RITM model. Custom model trained on the basis of RITM in Supervisely significantly reduced the number of required clicks, working time, correction counts, and overall time spent on data processing.
Surprisingly, SAM performs less effectively than RITM. A customized RITM operates 3.6 times faster than SAM. Additionally, it's worth noting that post processing of SAM predictions require significnt additional time.
 The performance of the Custom model is the best among others. Color coding: Green indicates excellent, orange signifies average, and red means poor.
The performance of the Custom model is the best among others. Color coding: Green indicates excellent, orange signifies average, and red means poor.
Suppose three annotators are involved in labeling 20,000 images, each featuring 7-15 plants. If the pre-trained SAM model is used, each annotator would need approximately 8,800 minutes to process the entire workload. However, by utilizing a custom model trained in Supervisely, the time required for each participant reduces significantly to about 2,400 minutes. Thus, opting for the custom RITM model substantially decreases the time investment for each contributor compared to using the pre-trained SAM model.
In addition to these findings, we carried out additional experimentss, confirming that in numerous scenarios, custom models are the only effective solution to address a problem. For example, in this post we experimented with training a custom model for crack segmentation. Here we trained a custom smart tool for Semantic Segmentation task.
Step-by-step guide
In our example, we trained the model on leaves. Let's take a look at what the training process entailed
Step 1. Prepare & annotate data
It is important to collect a diverse set of images. You can find and use the dataset of potato leaves and weed leaves that we used for training in DatasetNinja
To train the model effectively, we need to annotate images with precise masks. Normally, labeling images for model training involves annotating the whole image, which can be complicated and time-consuming—especially when dealing with various complex shapes. However, with Instance Segmentation, you don't have to label the whole image. Selective labeling is sufficient to train our interactive assistant model.
Step 2. Train model
Here you can find a detailed step-by-step guide on model training in Supervisely.

Train RITM
Dashboard to configure, start and monitor training
It's essential to mention that we opted for the Instance segmentation parameter instead of the traditional Semantic Segmentation. The key distinguishing feature of Instance Segmentation is that it distinguishes between object instances and outlines the boundaries of each object, and creating separate masks for distinct objects, even when they overlap or are close to each other.
Also, make sure that you opt for Crop to Fit an Instance Object option for selecting areas of the image with objects. It allows you to crop an image in a way that keeps objects as-is and prevents them from tearing or losing data.
To reproduce our experiment, it's recommended to use approximately the same parameters as indicated in the table below.
| Training hyperparameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Model | (COCO) HRnet18 IT-M |
| Input size | 512 x 512 |
| Number of objects | 466 weed and 210 Potato |
| Number of epochs | 20 |
| Batch size | 6 |
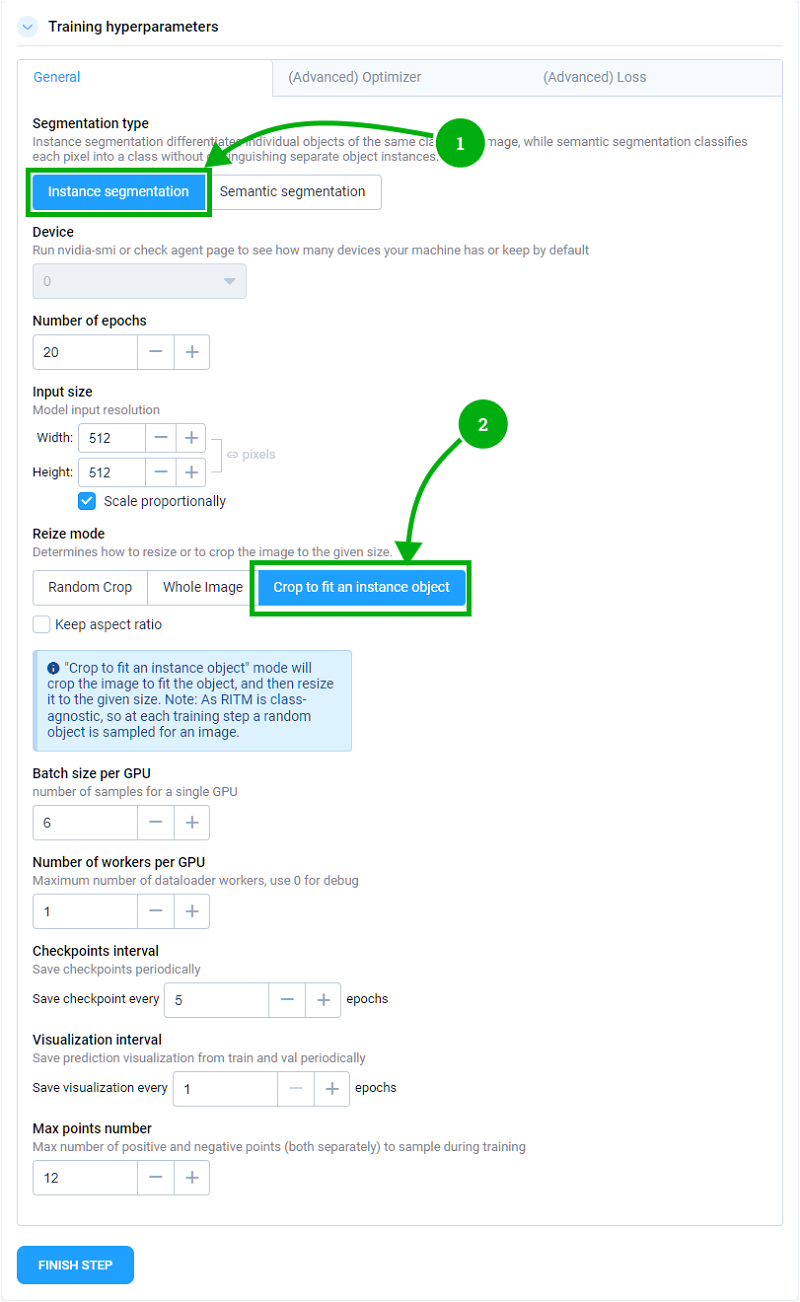 Training hyperparameters
Training hyperparameters
Training artifacts
After successful training, our Train RITM application saves resulting models to Team Files in the RITM_training folder. These files contain the "best checkpoint", the "last checkpoint" and any interval of checkpoints that you specify in the application. These files can be accessed and used by any member of your team.
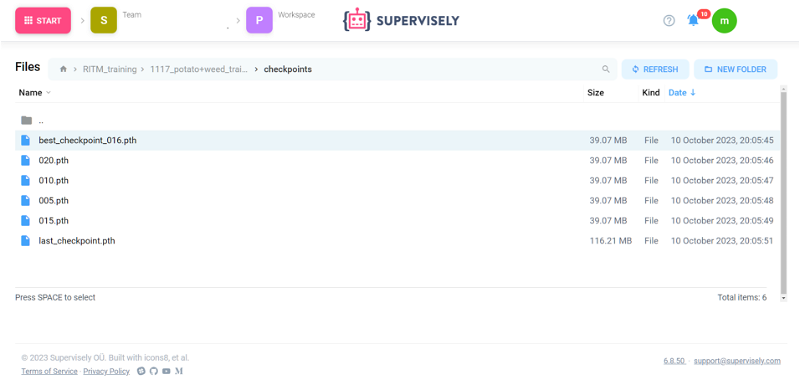 Model checkpoints in TeamFiles
Model checkpoints in TeamFiles
Step 3. Deploy your Custom Model
-
Find the desired checkpoint and copy its path.Go to
RITM_training➡️Name of your project➡️checkpoints, choose one of the checkpoints (we recommendbest_checkpoint) and copy its path. -
Launch the RITM application, select
Customand paste the file path. Supervisely App
Supervisely AppRITM interactive segmentation SmartTool
State-of-the art object segmentation model in Labeling Interface
-
Within the labeling tool, choose the custom model.
Step 4. Iterative Training for Model Improvement
This stage is about making the model better after testing it multiple times. We look at the test results to see where the model might be wrong or not making accurate predictions. Then, we redo the training process by making changes to the training data. Doing this over and over helps the model get better, making it more accurate and better at solving problems.
Conclusion
We created a model that successfully recognizes potato leaves and weeds using only a few objects in each image. This highlights the importance of innovations in labeling and computer vision to improve accuracy and performance in image processing.
We invite you to join the discussion and share your thoughts and experiences. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to ask in the public slack or via email at [email protected].
Thank you for joining us on this captivating journey into the world of Supervisely data labeling!
Supervisely for Computer Vision
Supervisely is online and on-premise platform that helps researchers and companies to build computer vision solutions. We cover the entire development pipeline: from data labeling of images, videos and 3D to model training.
The big difference from other products is that Supervisely is built like an OS with countless Supervisely Apps — interactive web-tools running in your browser, yet powered by Python. This allows to integrate all those awesome open-source machine learning tools and neural networks, enhance them with user interface and let everyone run them with a single click.
You can order a demo or try it yourself for free on our Community Edition — no credit card needed!